What is Kirchhoff's Law ?
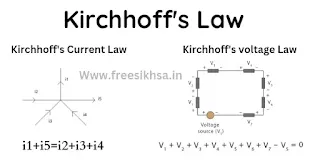
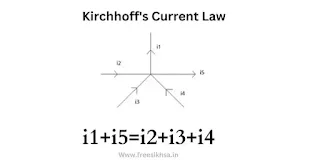
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL):
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the total amount of electric current flowing into a point in a circuit is equal to the total amount of current flowing out of that same point.
Explain: Total electric charge entering a junction must equal the total electric charge leaving the junction, as electric charge is conserved in a closed system. Therefore, the sum of all the currents entering in a junction must be equal to the sum of all the currents leaving that junction.
Mathematically, KCL can be expressed as:
∑I_in = ∑I_out
where, ∑I_in is the algebraic sum of all currents flowing into the junction and ∑I_out is the algebraic sum of all currents flowing out of the junction.
Example:
The current flowing through each branch is represented by I1, I2, and I3, and the resistors in the circuit are labeled as R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and RL. The load resistor RL represents the device or component that consumes power from the circuit.
To apply KCL, let's consider the current flowing into the junction at the top of the circuit. According to KCL, the sum of the currents entering the junction must be equal to the sum of the currents leaving the junction.
Let's assume that I1 = 2 A, I2 = 3 A, and I3 = 1 A. To find the current flowing through the load resistor RL, we need to apply KCL as follows:
∑I_in = ∑I_out
I1 + I2 + I3 = IL
2 A + 3 A + 1 A = IL
Simplifying the equation, we get:
IL = 6 A
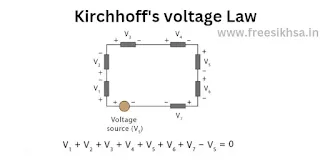
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)
∑V = 0
Example:
Use Of Kirchhoff's Law
- Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) is used to analyze circuits with multiple current paths and junctions. It helps in calculating the current flowing through each branch and junction of the circuit. Engineers use KCL to design and troubleshoot complex electrical circuits in various applications, such as power generation, transmission, and distribution systems, electronic devices, and control systems.
- Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) is used to analyze circuits with multiple voltage sources and loops. It helps in calculating the voltage drops across each component in the circuit. Engineers use KVL to design and troubleshoot complex electrical circuits in various applications, such as signal processing, communication systems, and control systems.